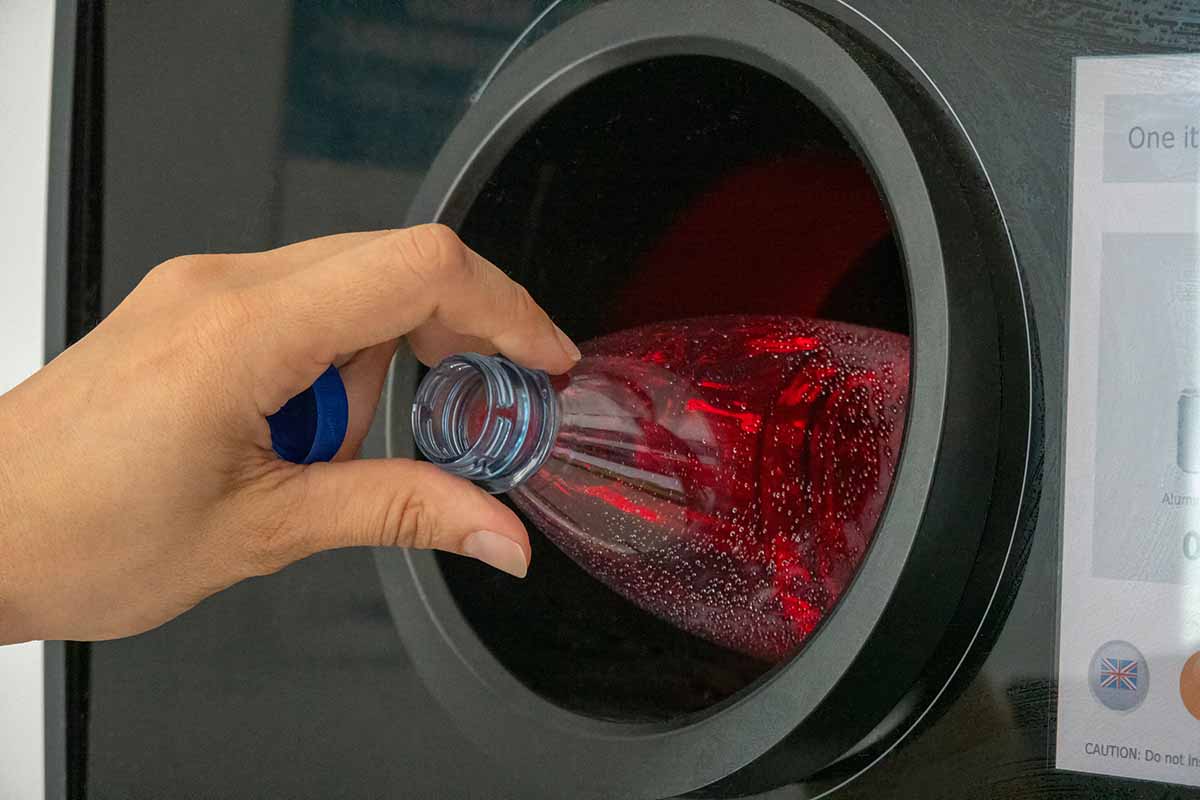
Oregon’s bottle bill, the oldest in the nation, could see some changes. | Veja/Shutterstock
Oregon state lawmakers recently approved a bill that allows the state to designate new redemption centers in Portland tailored toward canners — people who redeem containers on a daily or near-daily basis — and to allow retailers operating nearby to provide fewer redemption services. Continue Reading


 Colin Staub was a reporter and associate editor at Resource Recycling until August 2025.
Colin Staub was a reporter and associate editor at Resource Recycling until August 2025.