Lithium-ion battery fires are affecting all types of waste management and recycling facilities. But the U.S. EPA recently concluded that the municipal recycling sector has it worse than others.
An EPA report, published last month, comes as there is heightened attention on lithium-ion battery fires across many sectors of the waste management industry. For the report, EPA researchers examined MRFs, landfills, transfer stations, trucks, electronics recycling facilities, and other locations.
The report looked at the details of fires involving or suspected to involve lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) at 64 waste management facilities between 2013 and 2020. Details were gathered from news reports, expert interviews and other sources. Of the 64, researchers found 23 were MRFs, 13 were transport facilities, 10 were landfills and the remaining 18 were a variety of other facility types, including e-scrap processors, scrap metal yards, waste-to-energy plants and more.
“Our findings indicate that LIB fires are happening across the full spectrum of the waste management process, but MRFs appear to have faced the brunt of the negative impact,” the report states.
Of the MRFs that experienced battery fires in recent years, 78% had to call emergency responders at least once (compared with 40% of landfills), five of them had worker injuries (compared with just two other facilities across all other categories), and half of them experienced monetary loss.
MRFs also had the most instances of service disruption after a fire, the report added. As one example, the report pointed to a fire at a Republic Services facility in Scottsdale, Ariz.
“The fire burned for over a day and destroyed the facility, which caused the town of Fountain Hills, Ariz., to suspend its recycling program,” the report stated. “Recyclable material was taken to a landfill temporarily until the town found another MRF.”
How fires begin
The report ran through how a typical MRF might encounter and handle lithium-ion batteries, and how fires can be sparked.
“If spotted in the separation process, LIBs will be taken out of the MRF and sent to a specialty recycler or landfill,” researchers wrote. “If LIBs go unnoticed, they may become damaged by the sorting process.”
The increase in batteries entering MRFs is “forcing workers in these facilities to become de facto experts at spotting the batteries and extinguishing the fires that they inevitably ignite,” the report found.
If they make it to the sorting line, the batteries are typically jostled against other materials, leading to potential battery damage and fires.
“Conveyor belts may then send smoldering batteries throughout the facility unless the belts are stopped,” the report stated. “Furthermore, MRFs are full of flammable material. When fires do start, they may spread quickly due to the large amounts of paper and cardboard present.”
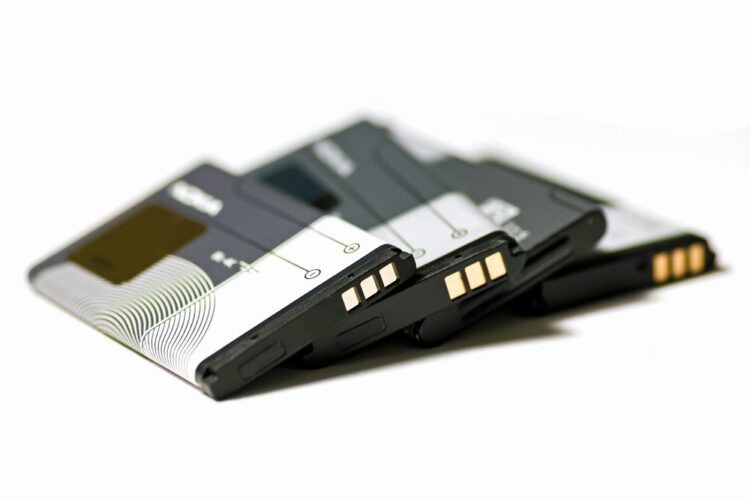
Batteries are also entering the waste stream in a growing number of products, the report found. Consumers might not consider the fire danger posed by the products, it added, giving the example of rechargeable plastic earbuds with a small embedded battery inside. There are no standardized labels for batteries in the U.S., and the caution language on batteries is sometimes misread by consumers to mean the battery is recyclable, the report stated.
The most common devices that led to fires were batteries from cell phones, tablets and laptops.
The findings were based on battery fires at the following facilities:
- Waste Management Little Rock Recovery Facility in Little Rock, Ark.
- Friedman Recycling in Tucson, Ariz.
- Republic Services in Scottsdale, Ariz.
- Marin Recycling Center in San Rafael, Calif.
- Shoreway Environmental Center in San Carlos, Calif.
- Larimer County Landfill’s Recycling Center in Fort Collins, Colo.
- Scott Area Recycling Facility in Davenport, Iowa.
- Mack’s Twin City Recycling in Urbana, Ill.
- Republic Services in Indianapolis.
- Ecomaine in Portland, Maine.
- Resource Recovery and Recycling Authority of Southwest Oakland County in Southfield, Mich.
- Southeastern Oakland County Resource Recovery Authority in Troy, Mich.
- Dem-Con Recycling in Blaine, Minn.
- Friedman Recycling in Albuquerque.
- Royal Waste Services in New York City.
- Taylor Garbage in Apalachin, N.Y.
- Rumpke Waste & Recycling in Cincinnati.
- North Lincoln Sanitary Service Recycle Center in Lincoln City, Ore.
- Fort Hood Recycle in Fort Hood, Texas.
- Republic Services in Plano, Texas.
- Chittenden Solid Waste District Recycling Facility in Williston, Vt.
- John’s Disposal in Norway, Wis.
- Outagamie County Recycling & Solid Waste in Appleton, Wis.
Impacts extend beyond immediate damage
Besides injuring workers and damaging specific facilities, battery fires are impacting the MRF sector as a whole in a few ways.
For one, the fire potential is creating substantial financial pressure on municipal recycling facilities.
“Multiple MRF operators consulted for this report indicated that their insurance premiums and deductibles have increased in recent years,” researchers wrote. “Not only are prices increasing, but insurers are leaving the market, making it more difficult for MRFs to get insurance.”
For a MRF in the San Francisco Bay Area that experienced a high-profile fire a few years ago, insurance is now divided among seven separate policies “because no single insurer is willing to bear the risk,” the report stated.
Facilities are also investing in suppression systems as a way to reduce their insurance rates, but such investments carry high costs, according to the report. These preventative measures are “shifting where monetary expenditures occur rather than preventing monetary impacts entirely,” researchers found.
Ultimately, the financial strain could make its way back to the ratepayers, if MRFs are forced to raise rates to cover higher insurance and other costs.
“This could leave Americans stuck with the bill for addressing the myriad issues created by LIBs inappropriately entering the municipal waste management process,” the report stated.